‘Co-Bots’ deployed in hospitals for delivering food, water and medicines to COVID-19 patients, has found a place in the compendium of effective Covid-19 practices, put together by NITI Aayog. The document titled ‘Mitigation and Management of COVID-19: Practices from Indian States and Union Territories’ mentions States and UTs that implemented several practices to enhance the effectiveness of COVID prevention and management initiatives in their local context.
An email was sent to all states and union territories (UTs) in July, requesting them to share any practices or models that they believe had been useful for Covid-19 mitigation and management.
The purpose of the volume is to ‘take note of practices that are grounded in our realities. Instead of expecting every State to reinvent the wheel, dissemination of such practices allows them to learn from each other and help find solutions to common problems,” – Amitabh Kant, NITI Aayog CEO in his foreword.
Technology played a major role in implementing these effective tools to mitigate the impact of Covid-19.
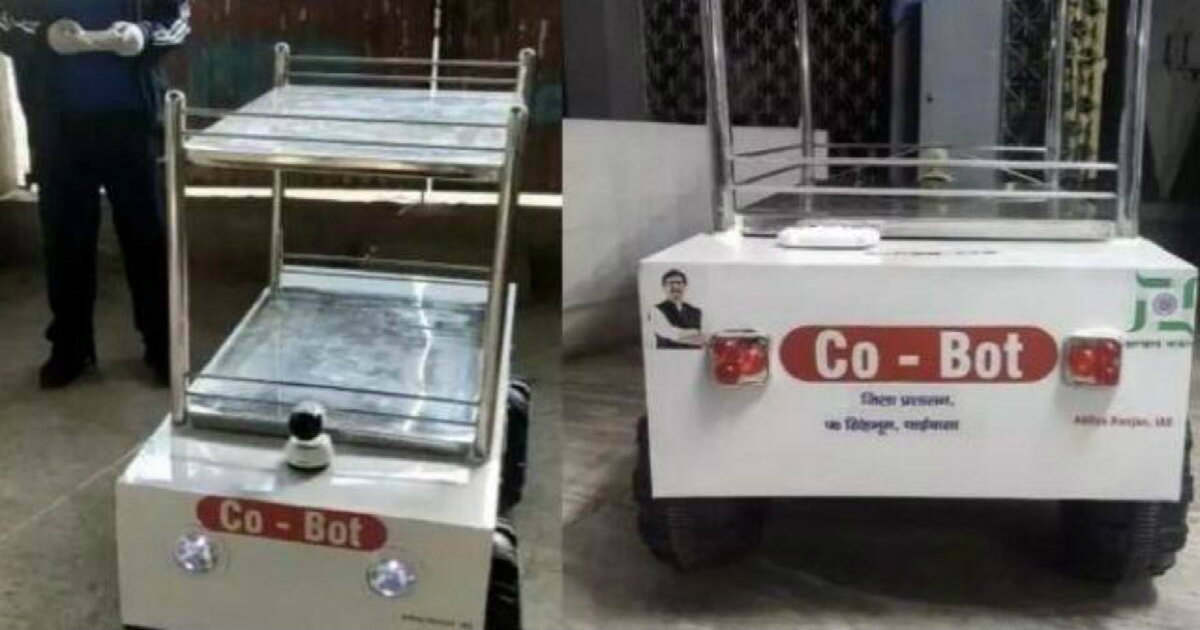
What are Co-Bots
- Jharkhand deployed Co-Bots in hospitals to minimize interaction between ancillary health workers/paramedical staff and COVID patients.
- The Co-Bots developed at Rs. 25,000 per Bot with a carrying capacity of 45 Kg operates with a remote within a 200 feet range.
- They are fitted with a Wi-Fi camera and microphone,
- They can move freely and operate remotely for two-way communication.
- They are also waterproof which makes it easy to sanitize them once they have been in contact with a patient.
- They are fitted with an ultrasonic obstacle warning system.
- Doctors can monitor patients remotely through Co-Bots and pass on necessary instructions through a microphone.
- Cameras also keep a vigil on the interaction between patients in isolation wards.
Another feature of the Co-bot is that it can serve food, water, medicines with a reduced risk of infection spread. A doctor or a nursing staff can view through the camera installed in the robot if the patient picks up the correct medicine or not. The speaker enables staff to communicate with the patient.
Apart from Jharkhand’s Co-Bots, the fever clinics in Mumbai’s Dharavi that helped control Covid-19 in Asia’s largest slum, mobile vans in Gujarat that dispensed non-Covid essential health services during the pandemic and Andhra Pradesh’s contact-tracing app that used mobile tower locations to trace the path taken by a positive patient and many other initiatives by different states have found a place in the compendium. NITI Aayog monitored how states innovated to stay ahead of the virus.